MSE: assess alertness, arousal, attention, language, cognition, memory, judgement, praxis, mood
CN EXAM: localize brainstem or peri-brainstem dysfunction
MOTOR: assess bulk/tone, power, abnormal movements
SENSATION: assess peripheral neuropathy or localize spinal cord dysfunction
REFLEXES: localize upper vs. lower motor neuron dysfunction
COORDINATION: assess dysfunction of cerebellum or its connections
STATION & GAIT: assess weakness, pain, and integration of sensory inputs with motor outputs
See below for details:
MSE: alertness, arousal, attention, language, cognition, memory, judgement, praxis, mood
Awake or in coma? How much stimulation to maintain arousal?
Orientation: person / place / time
Attention (20-->1 / Mon --> Sun / serial 7s / WORLD) and neglect (line bisection, letter cancelation, double simultaneous stimulation)
Language: follows commands, fluency, repetition, naming, articulation/dysarthria
Cognition: draw a clock-face and put in a specified time; administer MMSE/MOCA
Memory: STM (recall 3 objects), ITM (current events), LTM (past 5 presidents)
Insight/Judgment: e.g. awareness of deficits, recognizes own body parts, ?OCD sx
Praxis: brush teeth, comb hair, tie shoelaces
Calculation: $1.75 = how many quarters? (also finger agnosia, right/left confusion)
Affect/Mood – describe and say if they are congruent
CN EXAM: localize brainstem or peri-brainstem dysfunction (*=technically not CN)
Cranial Nerve 2
- Perform fundoscopic exam: examine retina and optic nerve head
- Evaluate visual acuity: Snellen card, OKNs
- Visual Fields: counting fingers in each visual quadrant or blink to threat
- Assess for RAPD (CN 2, 3)
Cranial Nerve 3, 4, 6
- Evaluate extraocular movements: H-test
- Examine for ptosis
- Assess pupillary reaction to light and accommodation
- Cover/Uncover Test for skew deviation
Cranial Nerve 5
- Check sensation in V1, V2, V3 distributions
- Assess temporalis muscle by asking patient to bite down
Cranial Nerve 7
- Assess facial symmetry and equal facial activation (check for nasolabial fold flattening and symmetric smile)
- Check taste on anterior 1/3 of the tongue (Each side of tongue controlled by ipsilateral facial nerve)
Cranial Nerve 8
- Evaluate hearing with whispered voice test or finger rub
- Perform Weber/Rinne test with 512Hz tuning fork
Cranial Nerve 9, 10
- Evaluate palate elevation by asking patient to say "ah"
- Gag reflex (afferent limb CN 9; efferent limb CN 10)
Cranial Nerve 11
- Check trapezius strength with shoulder shrug
- Check sternocleidomastoid strength with head turn against resistance
Cranial Nerve 12
- Evaluate whether tongue is midline by asking patient to stick tongue out
MOTOR: bulk/tone, power, abnormal movements
Assess bulk; assess tone - flaccid/rigid/spastic/paratonia/myotonia
Pronator drift/forearm rolling – corticospinal tract dysfunction (upward drift = parietal dysfunction)
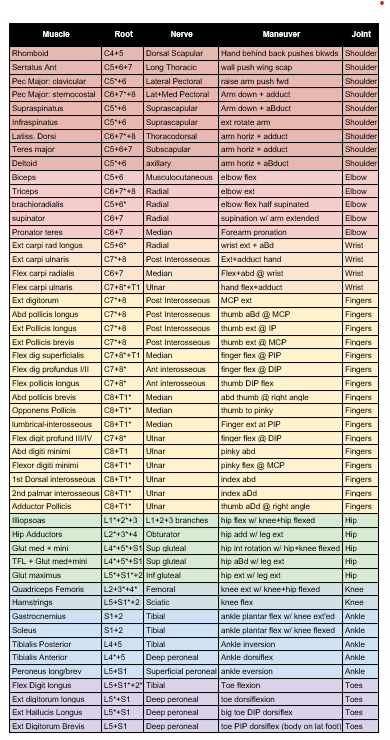
Individual muscle testing per chart below. Always stabilize proximal to the joint.
Graded: 0 none | 1 twitch | 2 move in plane | 3 antigravity | 4/4+/5- weak | 5 Full
Evaluate for subtle weakness with maneuvers such as finger taps and orbiting
SENSATION: touch, pain/pin, temperature, vibration, proprioception
Light touch (= control; if not present, further testing is not helpful for localization)
Spinothalamic tract: pinprick and temperature
Dorsal Columns: vibration (128Hz tuning fork), proprioception, two-point discrimination
REFLEXES: biceps, brachioradialis, triceps, patellar, achilles
Graded: 1+ slight | 2+ normal | 3+ brisk, often spread | 4+ elicited clonus
Brachioradialis and biceps reflexes – C5,6 (C5, C6 "pick up sticks")
Triceps reflex – C7, C8 (C7, C8 "open the gate")
Patellar reflex – L3, L4 (L3, L4 "kick in the door")
Achilles reflex - S1, S2 (S1, S2 "buckle my shoe")
Pathologic Reflexes
- Babinski Sign
- Hoffman's Sign
- Jaw Jerk
- Pectoral Spread
Primitive Reflexes (aka Frontal Release Signs)
- Glabellar: performed by repetitive tapping of the glabella (area between the eye brows); positive reflex is nonsuppression of blinking
- Palmomental: performed by stroking the thenar eminence; positive reflex is involuntary contraction of the mentalis muscle
- Rooting: performed by stroking the chin, mouth, or cheek; positive reflex is involuntary turning of the head toward the stimuli
- Snout: performed by tapping of the closed lips: positive reflex is contraction of the muscles that causes a snout
COORDINATION
Finger-nose-finger in upper extremities; in lowers, heel-to-shin or toe-to-finger
Rapid alternating movements: palm-dorsum-palm
Loss of check
Finger ChaseHold tip of pinky (or index) in one hand to the tip of the pinky in the other
STATION & GAIT
Walk across the room
Walk on heels (tests ankle dorsiflexion strength) and toes (plantar flexion strength)
Heel to toe (tandem)
Further features: antalgia, focal weakness (e.g. steppage), proper cane usage
Romberg sign (can’t stand eyes closed & feet together >60s 🡪 sensory ataxia)