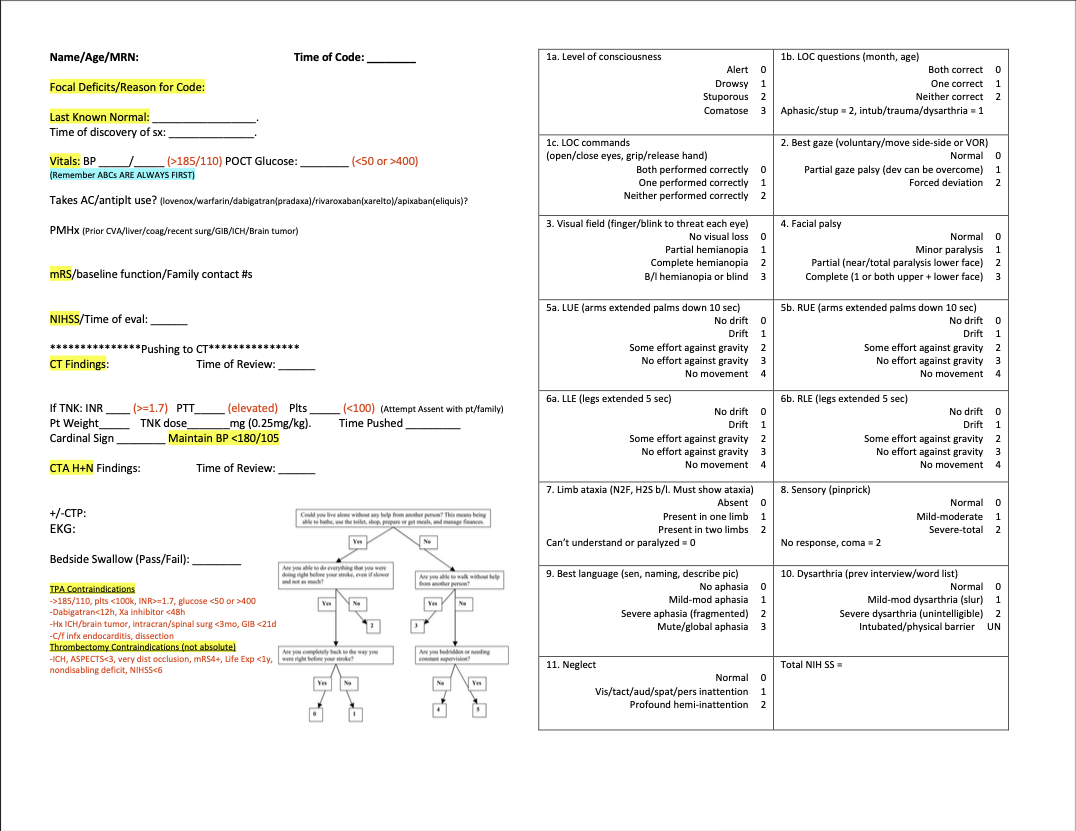
Initial Information to Obtain
- LKW: Last known well (DON’T TRUST ED/EMS TIME) or TOD: Time of Discovery!
- Precisely characterize timing and deficit
- Contraindications to tPA administration (see full protocol)
- CVA risk factors (DM, Cholesterol, HTN, Renal Failure, prior CVA/TIA, AFib, CAD)
- Medications - always ask about ASA/anticoagulants
- Blood Pressure, Glucose Measurements
- NIHSS Stroke Score (atleast perform relevant tests; can always complete after imaging)
Imaging
- Get plain head CT and simultaneously call stroke fellow (or senior on call or attending) immediately if patient is a possible tPA or LVO syndrome
- Obtain CT/CTA in all patients with suspected stroke
- If occlusion on CTA + LKW > 6H, will likely need CTP
- If LVO, discuss with stroke fellow and decide about posting on LVO WhatsApp Chat
TNK & Thrombectomy
- Make sure ED sends labs (especially CBC, Chem-7, coags, glucose, troponin)
- Consider all contraindications to tPA
- Can administer tPA without labs in many instances. (Exceptions: if patient is known to be on anticoagulation: always wait for coag panel).
- If TNK only, then patient should go to RESUS & use "Post Tenecteplase/Alteplase Stroke Neurology Adult Admission"
- If TNK + LVO, patient should get TNK either in radiology suite or RESUS then be transported to IR Room
- If LVO, then patient should be transported to IR room from either radiology suite or RESUS bay
Post Acute Management
- Post TNK patients can be admitted to stroke floor
- Post INR patients should go to NSICU
- If no acute management + stroke is suspected, discuss with stroke fellow about further management (wait for MRI vs immediate admission)
- All stroke patients should be made NPO until you perform swallow eval.
- NO ANTIPLATELETS or ANTICOAGULATION (INCLUDING DVT PROPHYLAXIS) FOR 24 HRS IF PATIENT RECEIVED TNK
- If not otherwise contraindicated, all stroke patients should receive at least ASA 81 mg
- If Afib, then can start ASA 81 (+/- DAPT) until time to restart AC
~ Diagram By Dr. Ken Leung